Sugar Technical Analysis Summary
Buy Stop։ Above 19.15
Stop Loss: Below 17.35
| Indicator | Signal |
|---|---|
| RSI | Buy |
| MACD | Neutral |
| MA(200) | Buy |
| Fractals | Neutral |
| Parabolic SAR | Buy |
| Bollinger Bands | Neutral |
Sugar Chart Analysis
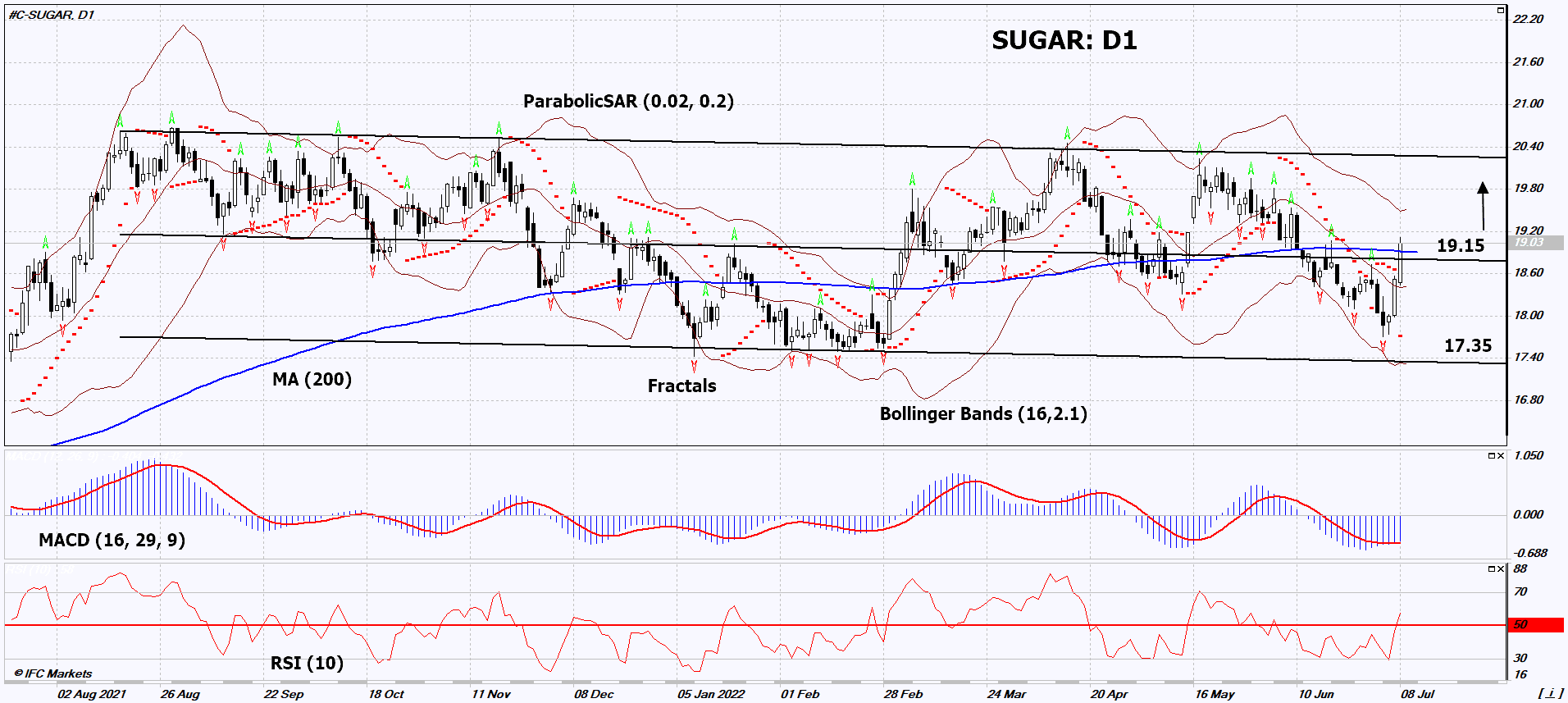
Sugar Technical Analysis
On the daily timeframe, SUGAR: D1 is moving towards the upper border of a wide neutral range. A number of technical analysis indicators formed signals for further growth. We do not rule out a bullish movement if SUGAR: D1 rises above its most recent high of 19.15. This level can be used as an entry point. Initial risk cap is possible below the 200-day moving average and the latest down fractal and lower Bollinger band: 17.35. After opening a pending order, we move the stop following the Bollinger and Parabolic signals to the next fractal low. Thus, we change the potential profit/loss ratio in our favor. The most cautious traders after making a trade can switch to a four-hour chart and set a stop loss, moving it in the direction of movement. If the price overcomes the stop level (17.35) without activating the order (19.15), it is recommended to delete the order: there are internal changes in the market that were not taken into account.
Fundamental Analysis of Commodities - Sugar
India is in no hurry to restore sugar exports. Will the SUGAR quotes continue to rise?
In May this year, the Indian authorities, for the first time in 6 years, limited the export of sugar in order to secure the domestic market. At the same time, sugar producers were given an export quota of 0.8 million tons. It was valid until July 5, but on Friday it was extended until July 20 due to the slow pace of shipments of Indian sugar to foreign buyers. Theoretically, this could be a sign of a slowdown in exports. Earlier in the 2021/2022 agricultural season, USDA predicted a record 8.8 million tons of sugar exports from India. At the same time, in the 2022/2023 season, it should already be reduced to 5.2 million tons. India and Brazil are the world’s largest sugar producers with 35-36 million tons per year each, and the global sugar production is about 182 million tons. Brazil is also the world’s largest exporter (26.6 million tons). India is in 3rd place in world sugar exports, and Thailand is in 2nd place (11 million tons). Another negative factor for sugar may be relatively expensive oil. This could increase the processing of sugar cane into motor fuel (ethanol) in Brazil and the US.